
Before you start reading this article about Solar Telescopes, one thing you should always remember is to never look at the sun directly through your telescope. Looking directly at the sun with a telescope will end up causing permanent damage to your eyes.
What exactly is a solar telescope?
Our sun is the closest star we have & observing the sun is very fascinating. There’s nothing like the thrilling experience of viewing the Sun through a solar telescope. The most efficient & exciting way to view the Sun is by zeroing in on a specific, narrow bandwidth of light. This narrow bandwidth of light is the hydrogen-alpha or H-alpha bandwidth. The light arriving from the sun at H-alpha frequency is coming from the layer of hydrogen gas just above the photosphere. To see this light we need to filter all the other bright bandwidths of light, only then you will be able to see the sun in this frequency. To achieve this, you need a dedicated solar telescope.
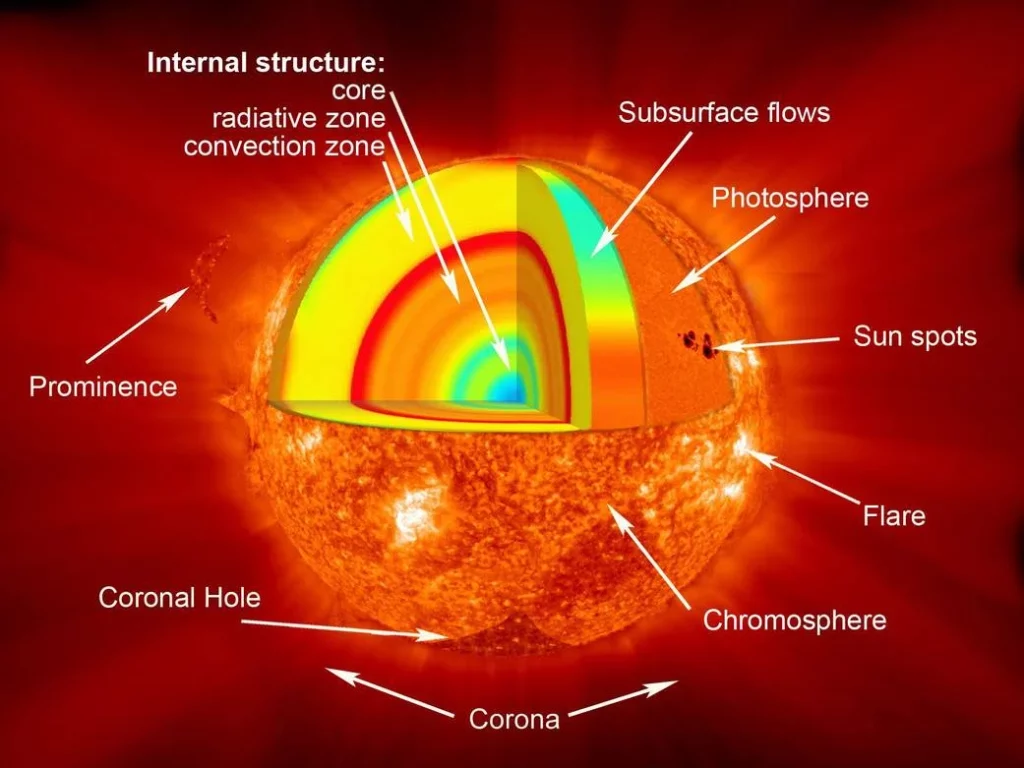
The solar telescope is very different from your normal telescope. A normal telescope is for observation of the cosmos during nighttime. A solar telescope you can use only during the daytime.
Types of solar filters for telescopes
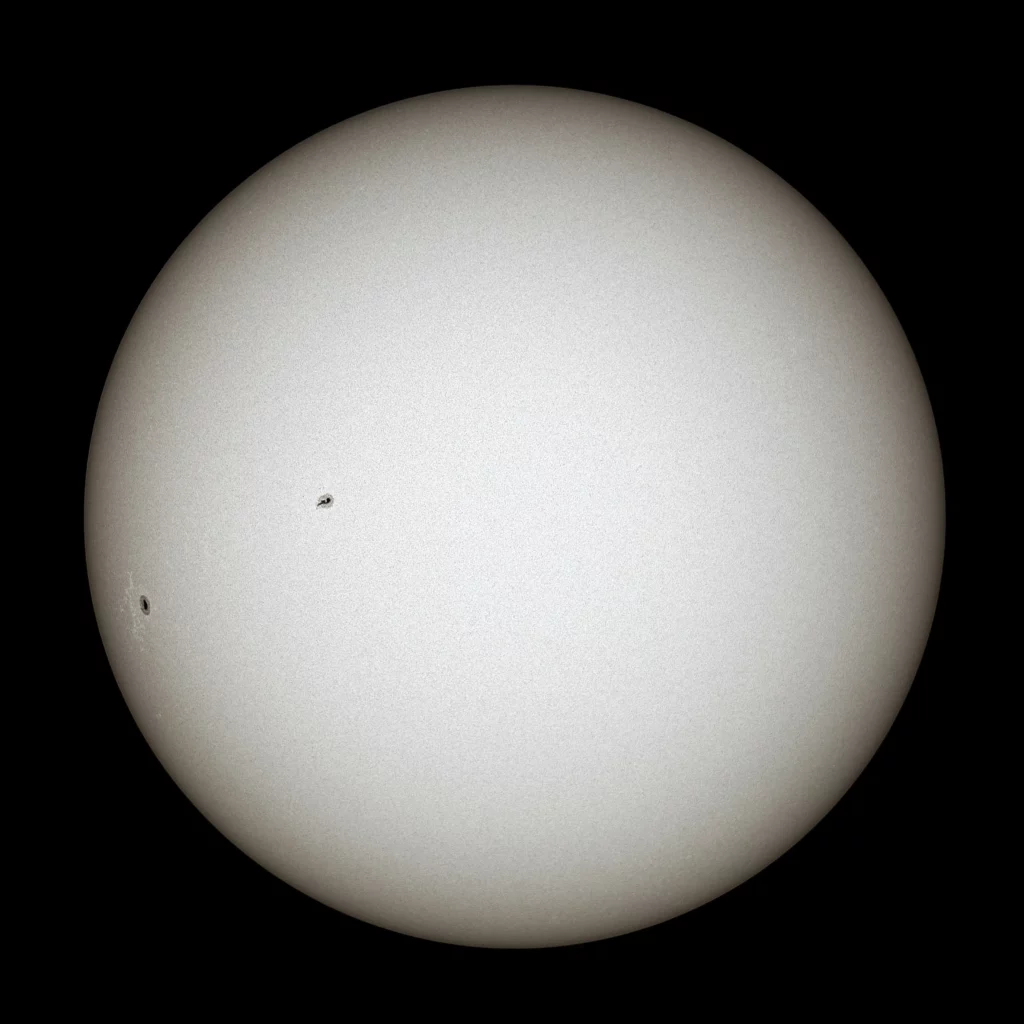
White light filter
There are various ways to observe the sun. If you have a normal telescope then you can use the white filter to see the sun. This white filter will filter out all the other wavelengths and will show you the sun in white. Before you use any such filter, make sure the filter does not have any tiny holes or the layers of the filter are properly connected. When you use the white filter all you can see are the sunspots and that’s it. There is nothing much more you can observe with this filter.

Calcium-K filter
Another way you can see the sun is through Calcium-K filters. These filters will add solar observation capability to your astronomical telescope in the Calcium-K wavelength. The solar disk and its features are very hard to see visually at Calcium-K filters. Whatever you can see through this calcium filter completely depends quite strongly on the observer’s eye. Generally, younger observers’ eyes are not very sensitive to violet wavelength & they can see more details through the Calcium-K filter. However, older observers may be very sensitive to violet wavelength & they may find it difficult to see any details through this filter. So, most of the time this calcium-k filter is used for imaging only.
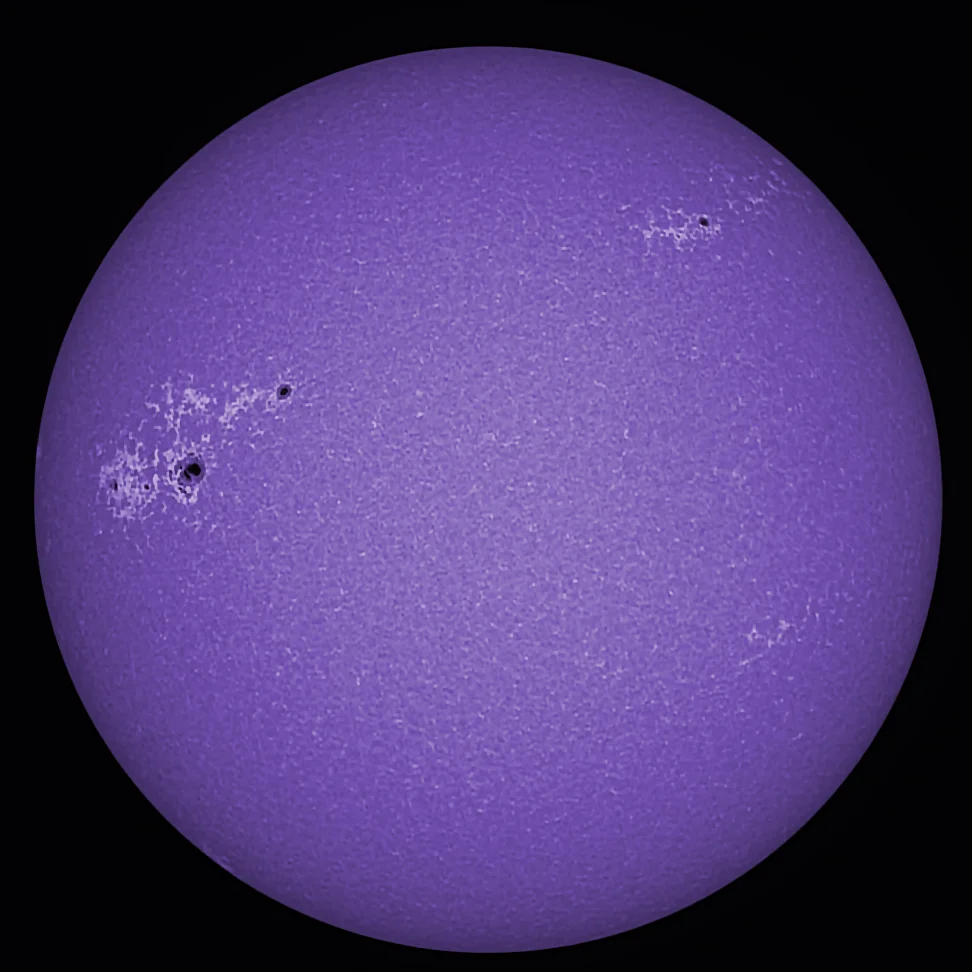
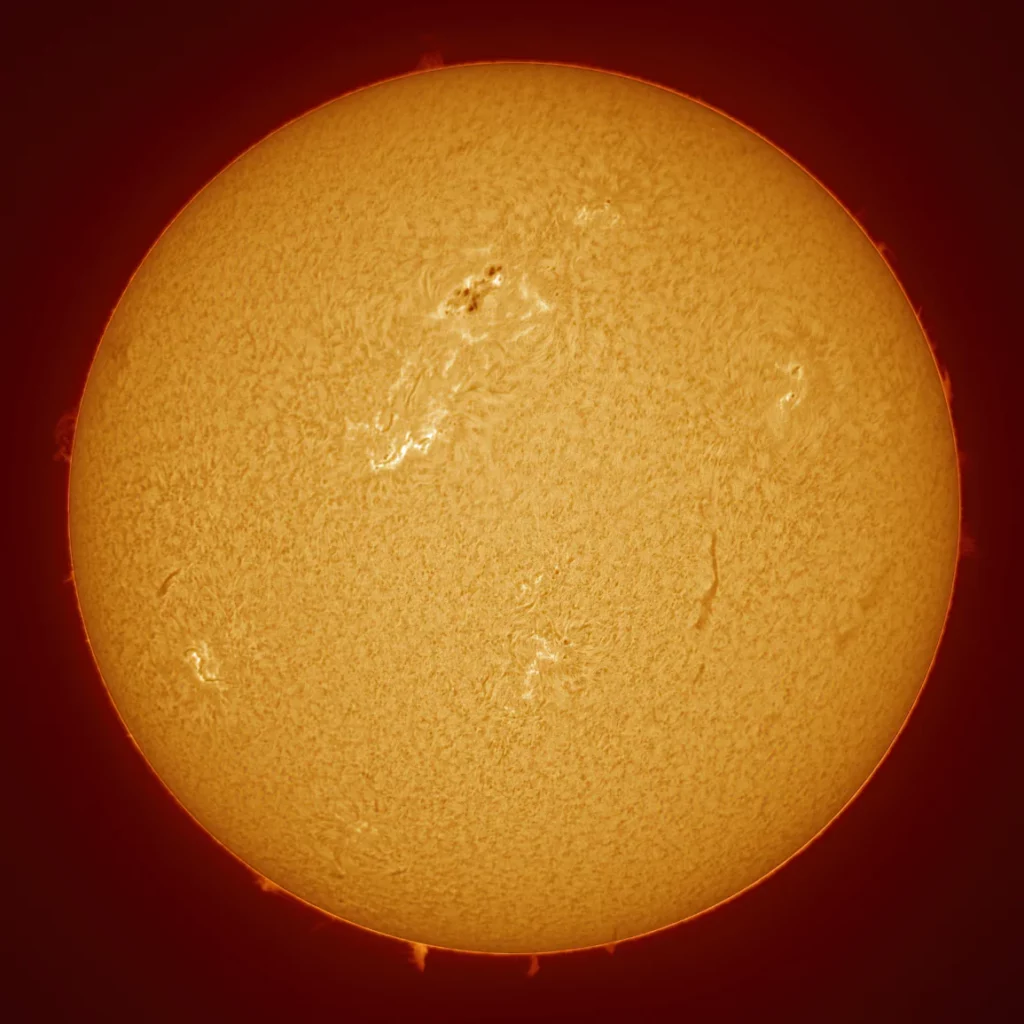
H-alpha Solar Telescope
The third way of observing the sun is through H-alpha solar telescope. If you ask any solar astronomer, they will often prefer H-alpha solar telescopes over white light filters or calcium-k filters. H-alpha solar telescopes are expensive but observers can see more details of the Sun. With these telescopes, you can see the sun’s changing chromospheres. You will be also able to see the filaments, prominence, plages, and much more with these H-alpha solar telescopes. The solar telescopes will not only protect your eyes from the Sun’s harmful rays but will enhance your viewing experience as well. Solar telescopes reduce glare and light scattering, increase contrast through selective filtration, increase definition and resolution, reduce irradiation, and lessen eye fatigue.

Solar Telescope Aperture
Usually, in a normal telescope, the aperture of a telescope is big. But the aperture of a solar telescope is not very big. Also, you don’t need a big aperture for a solar telescope. A normal telescope has to capture light coming from a distant star or a planet. So they need a big aperture to capture that distant source of light. But the sun is not very far and is very bright; you can’t even look at the sun with your naked eyes for very long. So the light emitted by the sun is excessive, for that you don’t need a big aperture. A small aperture will be enough for the solar telescope, that’s why these dedicated solar telescopes have very small apertures.

A solar telescope is a little more complicated than a normal telescope. It uses a multi-filter system with very precision. It consists of aperture, etalon size and its placement, safety filters, and out-of-band blocking.
How Do Solar Telescopes work?
Etalon
For getting into solar astronomy & to observe other details of the sun, you need a proper solar telescope. If you want to figure out what is right for you, then you need to have a basic understanding of different types of filters and different types of telescopes. Solar telescopes have something called “Etalon”. The etalon is the heart of the solar telescope. The etalon is nothing but a type of filter. Etalon consists of two parallel reflecting mirrors which give ultra-narrow bandpass.
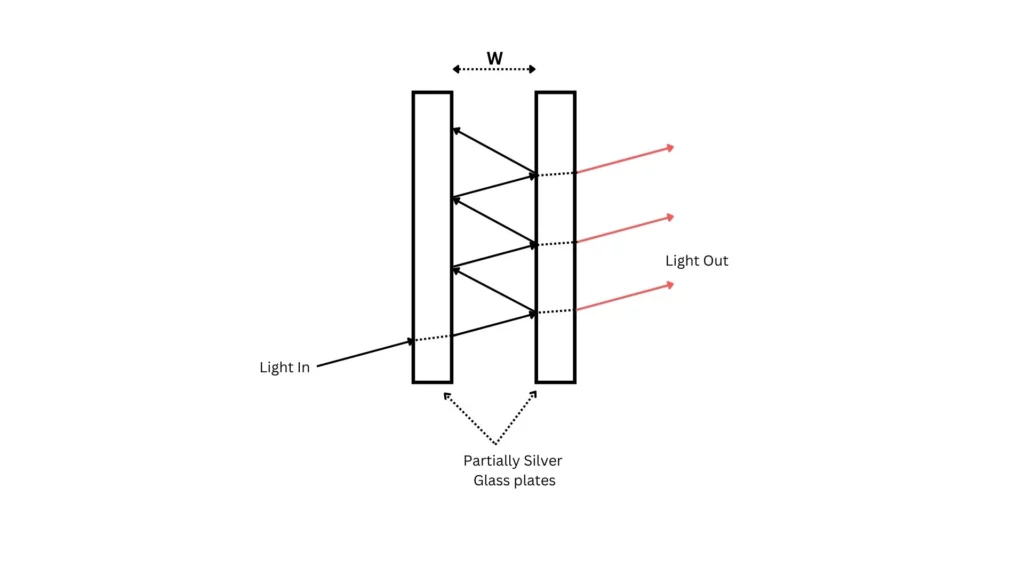
An etalon works as shown in the image above. It has two flat, parallel, semitransparent mirrors separated by a certain distance. This arrangement itself is an etalon. The light that enters the etalon and then goes through multiple reflections and the interference of the light emerging out from the etalon during each bounce causes a modulation in the transmitted and reflected beams. The resulting optical transmission is periodic in wavelength. Etalons are also used as precise wavelength references in telecommunication applications. They are mostly used to compare wavelengths and to study atomic spectra.

There are a few concepts or parameters regarding the etalon which you need to understand, to understand a solar telescope. These parameters are also mentioned in the specifications of many solar telescopes.
Bandpass.
Bandpass is the size of the gap between the reflective surfaces, and the reflectivity of the mirror coatings in etalon. If the mirrors in etalon have higher reflectivity then the bandpass will be narrower.
Peak transmission.
If the mirrors in the etalon have 100% reflectivity then no light would pass through the etalon. If the mirrors have zero percent reflectivity then all the light will pass through the etalon and there will be no band filtering for a particular wavelength. So the reflectivity of these mirrors is chosen between 0 to 100%. Usually, it transmits 60% of the light through the etalon. This 60 % is the peak transmission of the single etalon.
Etalon FWHM.
FWHM means full width half maximum. It is the width of the transmission profile at one-half of the filter’s maximum transmission. Or it is the width of a spectrum curve, measured between those points on the y-axis which are half the maximum amplitude. It is calculated in Angstrom.
Etalon FSR (free spectral range)
It is the distance between the two successive reflected or transmitted peaks of wavelengths by the etalon. It is also measured in Angstrom. If the gap between the etalon mirrors is less, then the free special range is more.
Etalon Net Finesse.
It is the ratio of free special range and bandpass. If the etalon net finesse is less, then it will not block ‘out of band’ leakage. In the case of finesse, the bigger is better, if the etalon finesse is 30 then it will have a good performance and will block ‘out of band’ leakages.
All these parameters mentioned are applicable to a single etalon. After the Etalon, there is a blocking filter in these telescopes. A Blocking Filters is essentially a cut-off filter. It’s a combination of several filters that are designed to provide additional safety to the viewer. It removes all out-of-band transmission from the etalon, allowing only the transmission at 656.28 nanometers also known as H-alpha to pass.
Filters in a Solar Telescope
A good solar telescope has an energy rejection filter, Etalon, Blue glass filter, Long Wave pass filter, blocking filter, Red glass filter, and Redundant Filters. All these filters, filter out the infrared & ultraviolet rays. As we mentioned in the beginning, the sun can cause permanent damage to your eyes. So, all these various filters are for the safety of the observer. This is the reason solar telescopes are quite expensive.
Single stack vs Double stack Solar Telescope
Usually, solar telescopes are categorized as single-stacked or double-stacked. A single-stacked solar telescope means it has only one etalon & a double-stacked solar telescope means it has two etalons. You get really good views of the sun with a double-stacked solar telescope and for most people, it is hard to go back to using a single-stacked solar telescope once they use a double-stacked solar telescope. Usually, with single stacking, the solar telescope is expensive with double stacking this telescope gets more expensive.

Best Solar Telescope to buy
Overall solar telescopes are expensive and it is for people who are very serious about solar astronomy. Some solar telescopes are mentioned below, you can check them out.
| Coronado telescope | BUY HERE |
| Lunt Solar 50 mm Ha Solar Telescope | BUY HERE |
| Lunt 80 mm Universal Day/Night/Solar Modular Telescope | BUY HERE |
| Lunt 40mm f/10 B500 Dedicated H-alpha Solar Telescope | BUY HERE |
We hope this article helped you to understand solar telescopes. If you want to learn more about stargazing then check other articles on our Website & YouTube channel.





